What is Present Tense
What is present tense: The present tense is one of the most common verb tenses in English, used to describe actions or states happening now or regularly. It plays a crucial role in both written and spoken communication. In this post, we will explore the types of present tense and how to use them effectively.
Let’s Start…
Types of Present Tense
The present tense is of four types. Namely,
- Simple present tense
- Present continuous tense
- Present perfect tense
- Present perfect continuous tense
what is the present tense
- The present tense is a verb form used to describe actions or situations happening now, in the present moment. It also describes regular actions, universal truths, or ongoing conditions. Essentially, it tells us what is happening right now or happens regularly.
- Examples:
- I go to school every day.
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- Usage: This tense is ideal for routines or facts. It’s often used with time expressions like “always,” “every day,” or “usually.”
Present simple tense rules
1. Basic Sentence Structure
In the presen’t simple tense, the structure of the sentence is straightforward:
- Subject + Base Verb (without “to”)
For example:
- I read books.
- They play football.
2. Third-Person Singular (He, She, It)
When the subject is he, she, or it, you need to add an -s or -es to the base form of the verb.
Rules for Third-Person Singular:
- Most verbs: Add -s to the verb.
- She runs every morning.
- He drinks tea.
- Verbs ending in -ch, -sh, -ss, -x, -o: Add -es.
- She watches TV.
- He goes to school.
- Verbs ending in consonant + y: Change the y to i and add -es.
- He tries hard.
- She flies to Paris.
3. Negative Sentences
To form a negative sentence in the present simple tense, use do not (don’t) or does not (doesn’t) with the base verb.
- Subject + Do/Does + Not + Base Verb
Examples:
- I do not like coffee. → I don’t like coffee.
- She does not eat meat. → She doesn’t eat meat.
Remember: In negative sentences, you don’t add -s or -es to the verb, even with third-person singular subjects.
- He doesn’t play the piano. (NOT He doesn’t plays the piano.)
Present simple tense examples / simple tense example
Here are 10 examples of sentences using the presen’t simple tense:
- She cooks dinner every evening.
- The sun rises in the east.
- They play soccer on Saturdays.
- He studies hard for his exams.
- We visit our grandparents during the holidays.
- Water freezes at 0°C.
- My dog barks when strangers come to the house.
- He loves to read mystery novels.
- I brush my teeth twice a day.
- The train leaves at 7 AM every morning.
present simple tense exercise
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in the present simple tense:
- She ______ (watch) TV every evening.
- They ______ (play) football on weekends.
- He ______ (read) a book every night before bed.
- The train ______ (leave) at 6 AM daily.
- My mother ______ (cook) delicious meals.
- The sun ______ (rise) in the east.
- I ______ (visit) my grandparents every summer.
- We ______ (go) to the gym twice a week.
- Water ______ (boil) at 100°C.
- She ______ (study) English at school.
Answer Key:
- watches
- play
- reads
- leaves
- cooks
- rises
- visit
- go
- boils
- studies

Present Continuous Tense / Present continuous
The present continuous tense is used to describe actions that are happening right now or actions that are ongoing in the present time. It emphasizes that the activity is in progress at the moment of speaking or around the current period.
Present continuous structure
he present continuous tense follows this structure:
- Subject + am/is/are + verb + -ing
Breakdown:
- Subject: The person or thing performing the action (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
- am/is/are: The correct form of the verb “to be” depending on the subject.
- Use am with “I.”
- Use is with “he,” “she,” and “it.”
- Use are with “you,” “we,” and “they.”
- Verb + -ing: The base form of the verb with -ing added to show the ongoing action.
1. Affirmative Form
- Subject + am/is/are + verb + -ing
For example:
- I am reading a book.
- She is playing the piano.
- They are running in the park.
2. Negative Form
To make a sentence negative, add not after am/is/are.
- Subject + am/is/are + not + verb + -ing
For example:
- I am not watching TV right now.
- He is not coming to the party.
- They are not playing outside.
3. Question Form
To form a question, place am/is/are before the subject.
- Am/Is/Are + Subject + verb + -ing?
For example:
- Are you reading a book?
- Is she cooking dinner?
- Am I doing this correctly?
present continuous tense examples
Here are 10 examples of sentences :
- I am reading a fascinating book right now.
- She is preparing dinner in the kitchen.
- They are playing football in the park.
- We are planning a trip to the mountains this weekend.
- He is learning how to play the guitar.
- The children are watching their favorite cartoons on TV.
- It is raining heavily outside at the moment.
- My friends are coming over for dinner tonight.
- The company is hiring new employees this month.
- You are improving your English skills by practicing daily.
Present continuous tense exercises
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in the present continuous tense:
- She ______ (write) an email to her friend right now.
- They ______ (play) outside in the yard.
- I ______ (wait) for the bus at the moment.
- We ______ (watch) a new movie tonight.
- He ______ (study) for his final exams this week.
- The baby ______ (cry) because she is hungry.
- You ______ (work) on your project, aren’t you?
- My parents ______ (visit) us next month.
- The teacher ______ (explain) the lesson to the students.
- It ______ (snow) heavily in the mountains.
Answers to Present Continuous Tense
- is writing
- are playing
- am waiting
- are watching
- is studying
- is crying
- are working
- are visiting
- is explaining
- is snowing
More Read:
Future Tense-example
What is Present perfect tense
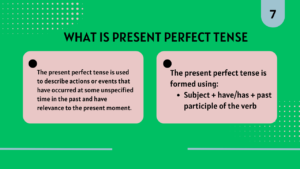
The present perfect tense is used to describe actions or events that have occurred at some unspecified time in the past and have relevance to the present moment. It emphasizes the connection between the past and the current situation rather than focusing on when the action took place.
Present perfect tense structure
The present perfect tense is formed using:
- Subject + have/has + past participle of the verb
Breakdown:
- Subject: Refers to the doer of the action (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
- have/has:
- Use “have” with the subjects I, you, we, and they.
- Use “has” with the subjects he, she, and it.
- Past Participle: The third form of the verb, which may be regular (adding -ed) or irregular.
- Experiences:
- It is often used to express experiences or actions that have happened at some point in the past without specifying when.
- Example: I have traveled to several countries.
- Recent Actions:
- It describes actions that have just been completed and may still have an effect on the present.
- Example: She has just finished her homework.
- Ongoing Situations:
- It indicates situations that started in the past and continue into the present.
- Example: They have lived in this city for five years.
- Achievements:
- It highlights accomplishments or milestones achieved up to the present.
- Example: He has won several awards for his work.
present perfect tense sentence
Here are 10 sentences using the present perfect tense:
- I have completed my assignment ahead of schedule.
- She has visited her grandparents twice this month.
- They have lived in this city for over ten years.
- We have seen that movie three times already.
- He has just finished his breakfast before heading to work.
- The team has won the championship for the last two seasons.
- You have learned a lot from this course so far.
- The children have played outside all afternoon.
- I have never tried sushi before.
- She has organized the files in alphabetical order.
present perfect tense exercise
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in the present perfect tense:
- I ______ (finish) my homework for today.
- She ______ (travel) to three different countries this year.
- They ______ (see) that band live twice.
- We ______ (not complete) the project yet.
- He ______ (never be) to a concert before.
- The children ______ (eat) all the cookies.
- You ______ (learn) a lot in this class so far.
- My parents ______ (visit) us several times this year.
- The weather ______ (change) significantly this week.
- She ______ (just call) to check on you.
Answer Key:
- have finished
- has traveled
- have seen
- have not completed
- has never been
- have eaten
- have learned
- have visited
- has changed
- has just called
Present perfect continuous tense
The present perfect continuous tense is used to express actions or situations that began in the past and are still continuing or have recently stopped, with an emphasis on the duration or ongoing nature of the action. It often highlights how long an action has been occurring up to the present moment.
Present perfect continuous tense formula
The present perfect continuous tense is formed using:
- Subject + have/has been + verb + -ing
Breakdown:
- Subject: The doer of the action (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
- have/has been:
- Use “have been” with the subjects I, you, we, and they.
- Use “has been” with the subjects he, she, and it.
- Verb + -ing: The base form of the verb with -ing added to show the ongoing action.
Usage of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Duration of Actions:
- It emphasizes how long an action has been happening.
- Example: I have been studying for three hours.
- Recent Activities:
- It can indicate actions that have recently stopped but still have relevance to the present.
- Example: She has been running, so she is out of breath.
- Repeated Actions:
- It can describe actions that have been happening repeatedly over a period.
- Example: They have been practicing the piano every day.
Key Time Expressions
The present perfect continuous tense is often used with time expressions such as:
- For: I have been waiting for an hour.
- Since: She has been working here since 2018.
- Lately: He has been feeling tired lately